TLDR: VulcanSQL, a free and open-source data API framework built specifically for data applications, empowers data professionals to generate and distribute data APIs quickly and effortlessly. It takes your SQL templates and transforms them into data APIs, with no backend expertise necessary.
Preface
Normally, in order to retrieve the data we need from a data source, we have to write SQL statements. However, this process could be time-consuming especially when the data consumers have different requirements in short time. Now, to make this process easier and more flexible to data consumers, VulcanSQL has integrated HuggingFace inference capabilities. This allows us to reduce the need for changing SQL templates by simply allowing data consumers to ask questions and getting the results they need.
VulcanSQL HuggingFace Filters
VulcanSQL leverages the Hugging Face Inference feature through the VulcanSQL Filters statement.
What is Hugging Face
Hugging Face is an AI community that builds tools to enable users to build, train, and deploy machine learning models. Hugging Face makes it easy to share tools, models, model weights, and datasets among other practitioners through its toolkit.
Hugging Face provides the Inference API feature that allows users to run pre-trained AI models for various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, making it easier to integrate powerful language models into applications and services.
Table Question Answering Task Filter
"Table Question Answering" is one of the NLP (Natural Language Processing) tasks provided by Hugging Face. Table Question Answering involves answering a question about the information in a given table. It allows for simulating SQL execution by inputting a table through its model.
VulcanSQL currently integrates the table question answering feature by creating the filter named
huggingface_table_question_answering and allows you to apply functions to variables using the
pipe operator (|).
Sample 1 - send the data from the set tag:
You could give the dataset with the set tag
and give the question with the query field:
{% set data = [
{
"repository": "vulcan-sql",
"topic": ["analytics", "data-lake", "data-warehouse", "api-builder"],
"description":"Create and share Data APIs fast! Data API framework for DuckDB, ClickHouse, Snowflake, BigQuery, PostgreSQL"
},
{
"repository": "accio",
"topic": ["data-analytics", "data-lake", "data-warehouse", "bussiness-intelligence"],
"description": "Query Your Data Warehouse Like Exploring One Big View."
},
{
"repository": "hello-world",
"topic": [],
"description": "Sample repository for testing"
}
] %}
-- The source data for "huggingface_table_question_answering" needs to be an array of objects.
SELECT {{ data | huggingface_table_question_answering(query="How many repositories related to data-lake topic?") }} as result
Here is a response returned by huggingface_table_question_answering:
[
{
"result": "{\"answer\":\"COUNT > vulcan-sql, accio\",\"coordinates\":[[0,0],[1,0]],\"cells\":[\"vulcan-sql\",\"accio\"],\"aggregator\":\"COUNT\"}"
}
]
The result will be converted to a JSON string from huggingface_table_question_answering.
You could decompress the JSON string and use the result by yourself.
Sample 2 - send the data from the req tag:
You could also use the req tag to keep the query result from the previous SQL condition and save it
to a variable named repositories. Then you can use .value() to get the data result and
pass it to huggingface_table_question_answering with the pipe operator |.
{% req repositories %}
SELECT * FROM read_csv_auto('Top200StaredRepositories.csv')
{% endreq %}
{% set question = context.params.question %}
SELECT {{ repositories.value() | huggingface_table_question_answering(query=question, wait_for_model=true) }} as result
You may see we also pass the value true to the wait_for_model field,
which means waiting for the HuggingFace table question answering to load the pre-trained model; otherwise it may fail due to the model not being loaded completely.
For more information, please see the VulcanSQL's Hugging Face Table Question Answering Filter Extension Documentation.
Now we could request API with different questions by the parameter question and get different results!
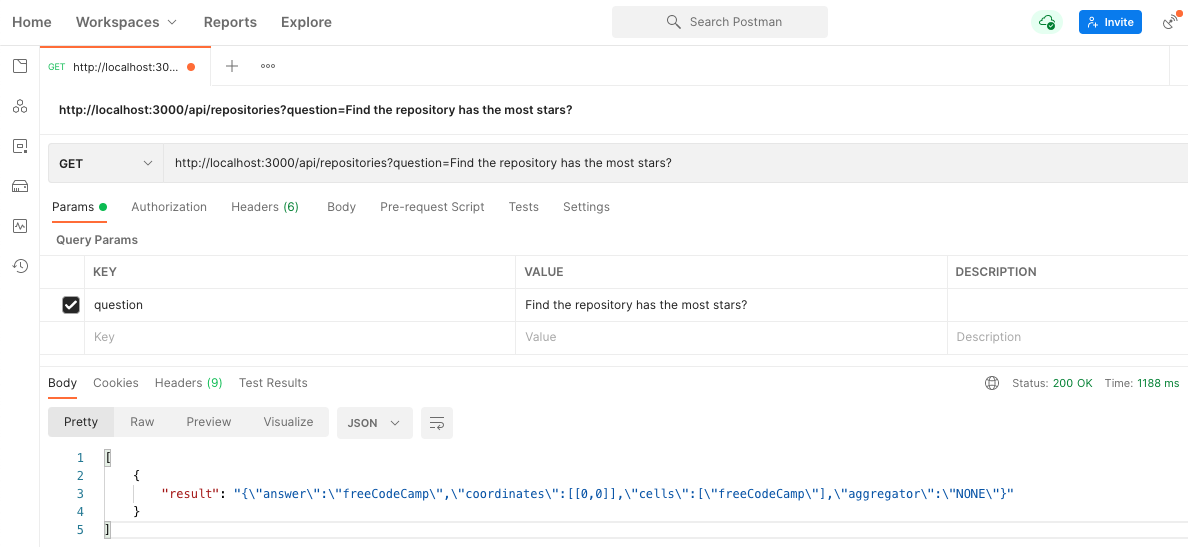
Scenario 1 - We asked Find the repository has the most stars?, and the Hugging Face model told us that freeCodeCamp has the most stars.
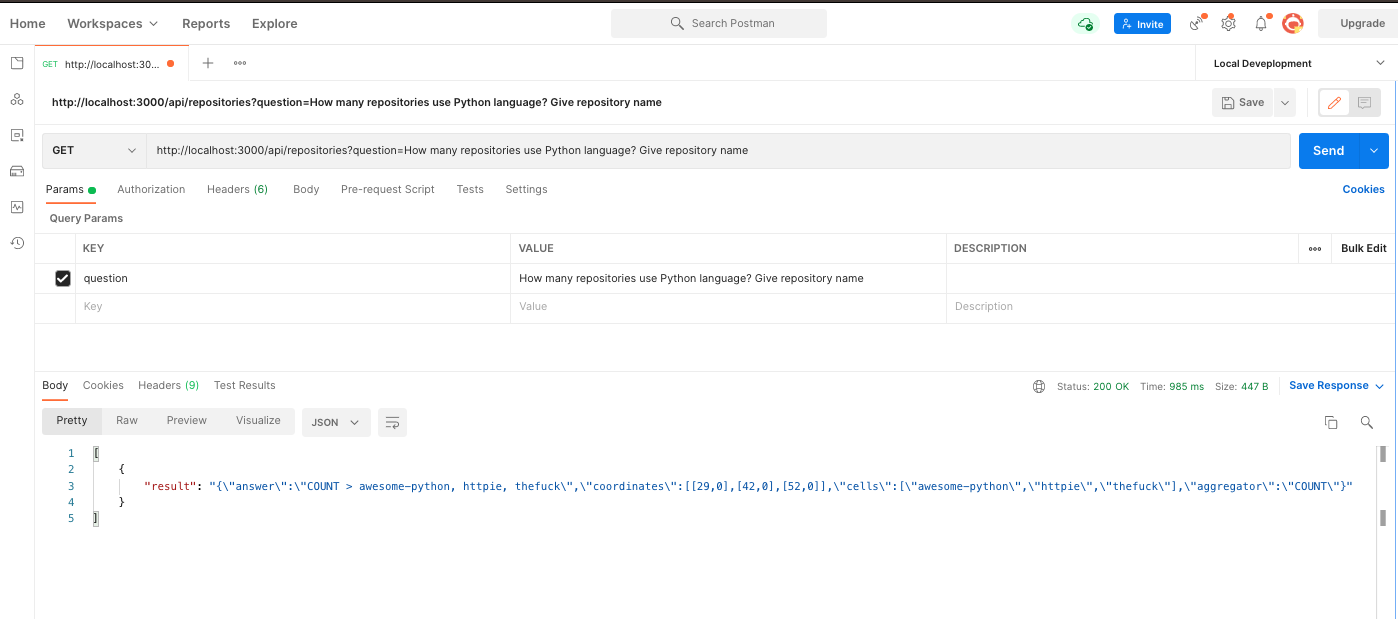
Scenario 2 - We asked How many repositories use Python language? Give repository name,
and the Hugging Face model told us awesome-python, httpie and thefuck are using Python language.
As you see, after using the HuggingFace Table Answering Filter, the benefit is:
- Don't need to change the SQL template file.
- Don't need to re-build the SQL template file.
- Don't need to create another SQL template file to satisfy two query scenarios.
The quality of response depends on the model used in the HuggingFace Table Answering Filter and how we ask the questions to the model.
However, VulcanSQL not only provides the Table Question Answering Filter feature but also publishes a popular Text Generation Filter for the Hugging Face Filters Extension.
It means you could use the popular models Meta Llama2! 🥳
Text Generation Task Filter
"Text Generation" is another NLP (Natural Language Processing) task provided by Hugging Face. Text generation means producing new text. These models can, for example, fill in incomplete text or paraphrase, or even answer your question according based on your input context.
VulcanSQL also integrates the text generation feature by creating the filter named
huggingface_text_generation and allows you to apply functions to variables using
the pipe operator (|).
Besides, Hugging Face provides the popular Meta Llama2 models, a collection of pre-trained and fine-tuned generative text models ranging in scale from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters.
In the next sample, we are going to demonstrate how VulcanSQL uses the huggingface_text_generation filter
with the Llama2 model meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf to answer your question.
If you would like to use the Meta Llama2 model, you have at least two options to choose from:
- Subscribe to the Hugging Face Pro Account.
- Use Hugging Face Inference Endpoints.
For more information, please see VulcanSQL's Text Generation Filter Extension Documentation.
Sample - send the data with the req tag:
The sample uses the HuggingFace access token of the Pro Account to get
the result by using the meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf model.
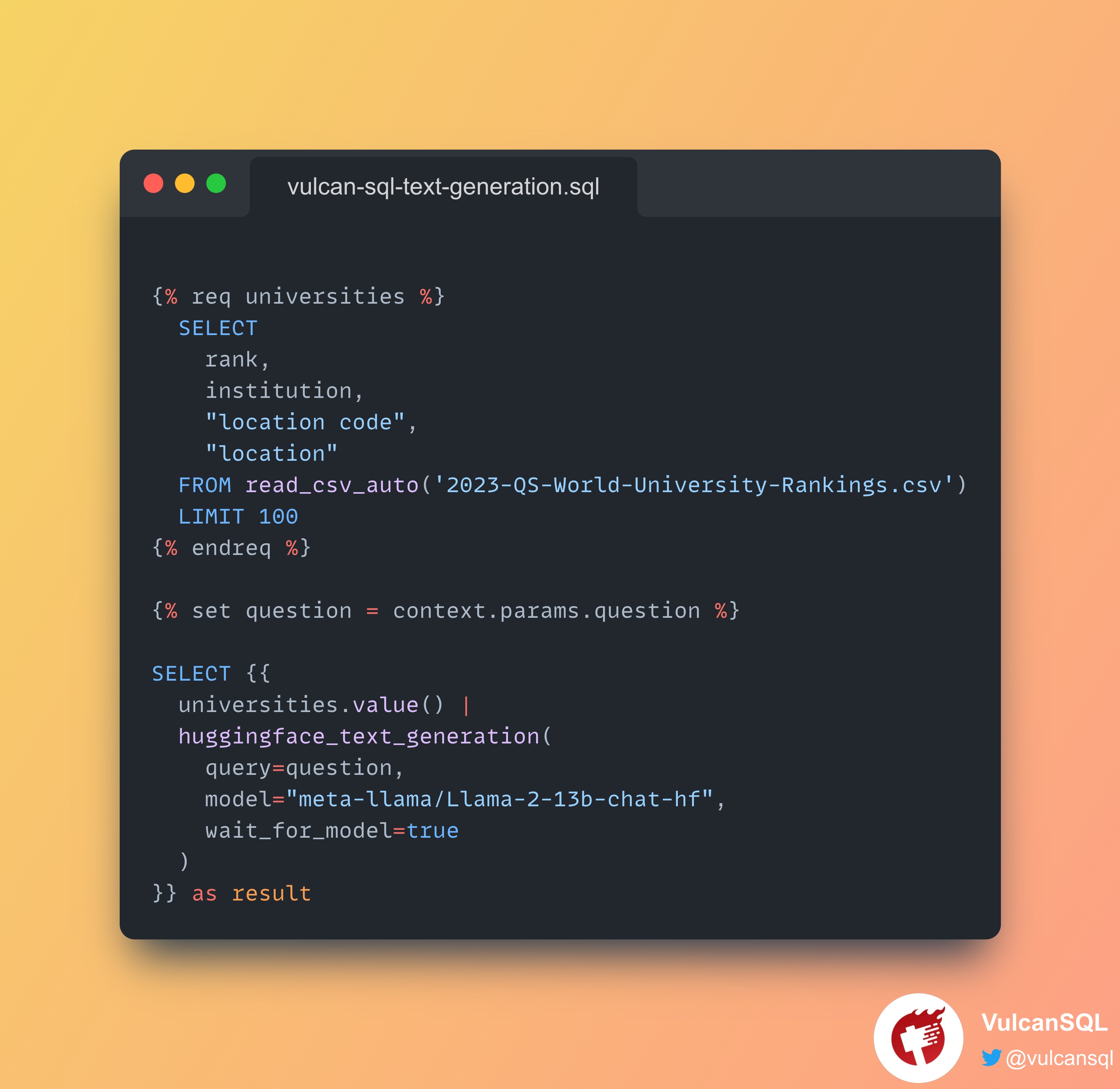
-- Using the `meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf` model, data must have less than 4096 tokens, so need to limit data row and column for universities.
{% req universities %}
SELECT rank, institution, "location code", "location" FROM read_csv_auto('2023-QS-World-University-Rankings.csv') LIMIT 100
{% endreq %}
{% set question = context.params.question %}
SELECT {{ universities.value() | huggingface_text_generation(query=question, model="meta-llama/Llama-2-13b-chat-hf", wait_for_model=true) }} as result
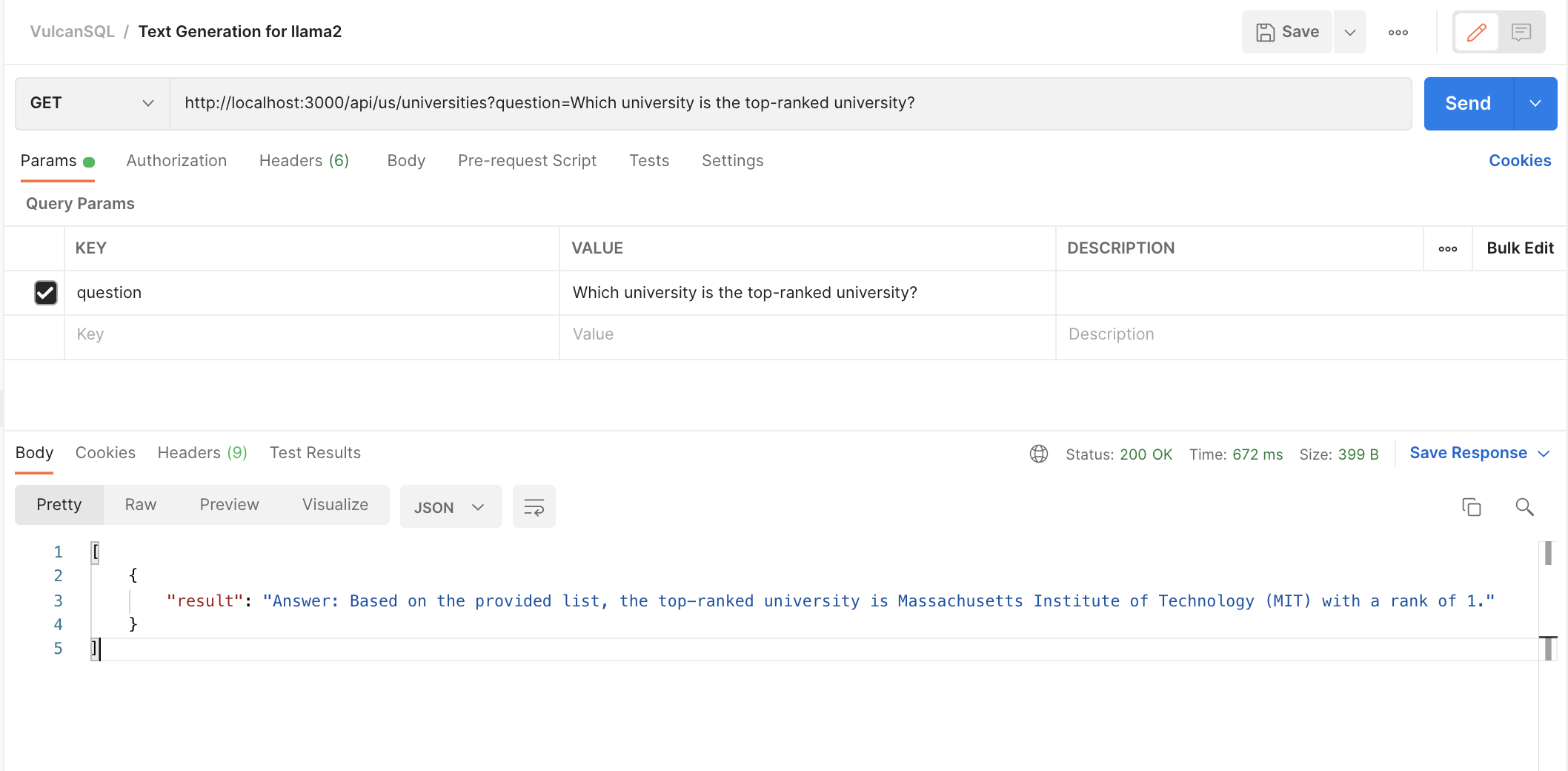
Scenario 1 - We asked Which university is the top-ranked university?, and the model gave us the top-ranked university.
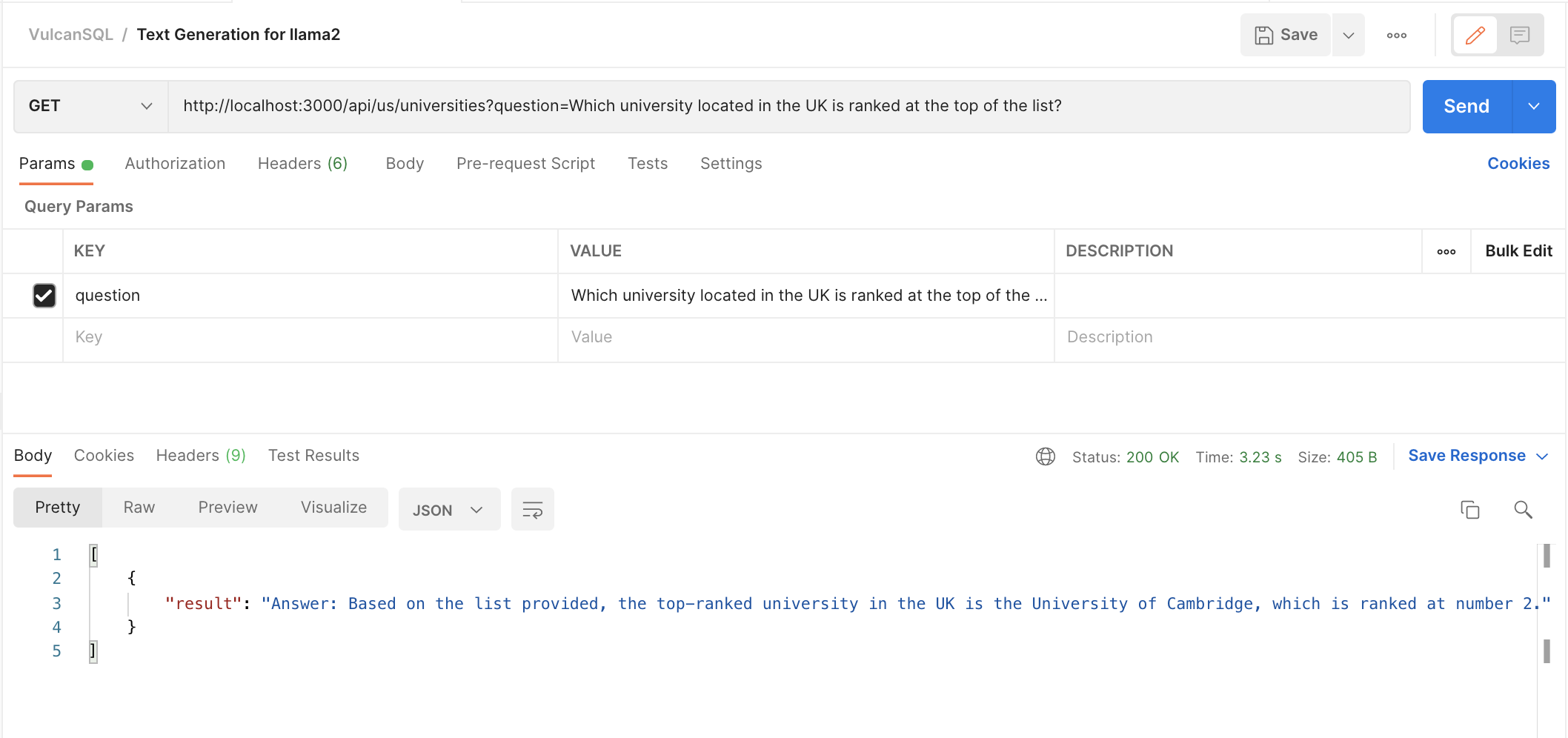
Scenario 2 - We asked Which university located in the UK is ranked at the top of the list?,
and the model gave us the top-ranked university that is located in the UK.
Wow! It's really amazing that the HuggingFace Text Generation Filter can answer your question based on the given dataset!
Conclusion
With more and more great machine learning models coming out, it's great that we can utilize their power to make our daily work easier! We hope this blog post can give you a glimpse on how VulcanSQL can be involved in this revolutionary event in human history!
Imaging a world that you can deliver APIs that users only need to query questions they have, the model handles SQL logic for you, and VulcanSQL takes care of the data privacy and API things. It sounds exciting, isn't it?
In the near future, we'll publish detailed step-by-step guides to help you write your own AI-enabled filter extensions! Stay tuned!